BONOXIL
Advanced Bone Health Formula with Calcium Citrate, Magnesium, Vitamin D3 & Vitamin K2-7

What is it?
Bonoxil is a scientifically developed bone support formulation designed to promote optimal calcium utilization, enhance bone mineralization, and support long-term skeletal strength. The formulation combines highly absorbable mineral forms with synergistic vitamins to help maintain structural integrity of bones and support musculoskeletal health.
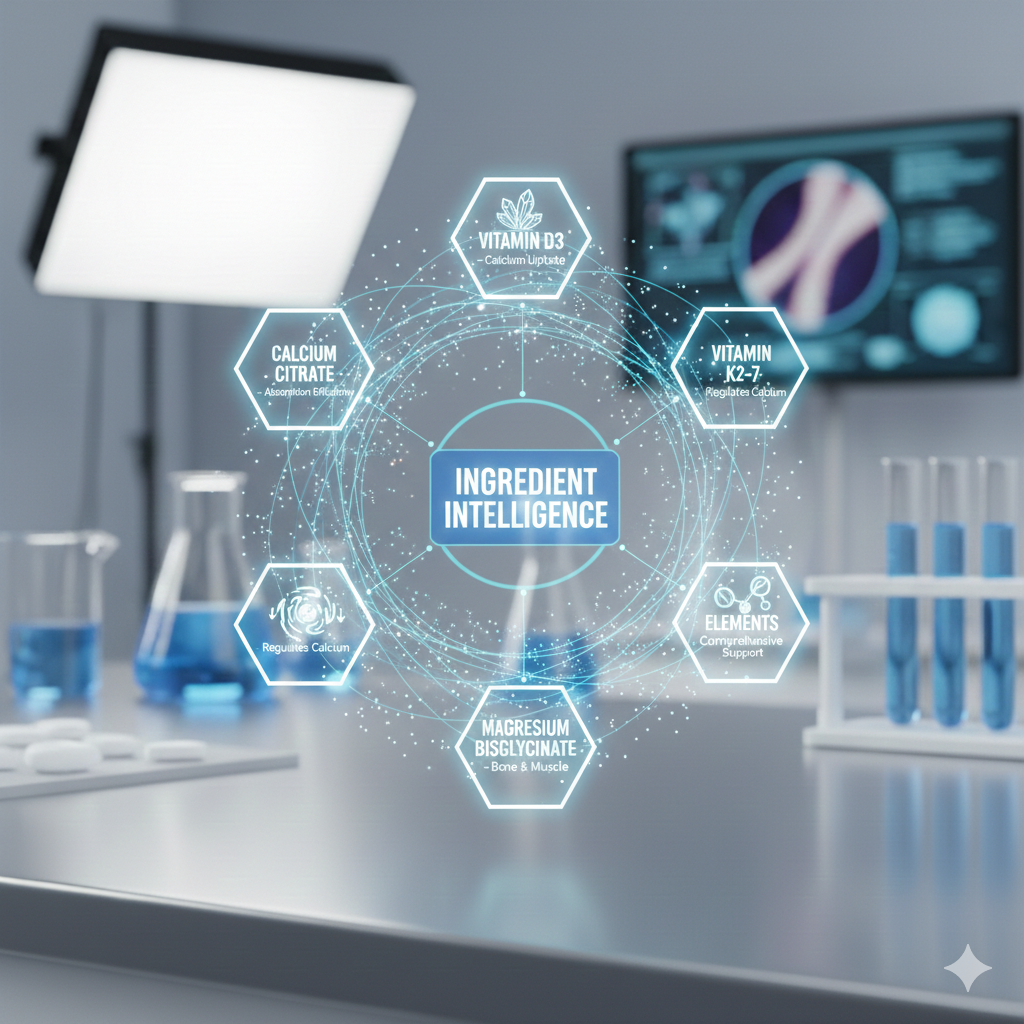
Ingredient Intelligence
Calcium Citrate – Selected for absorption efficiency and tolerability.
Vitamin D3 – Supports calcium uptake.
Vitamin K2-7 – Helps regulate calcium deposition.
Magnesium Bisglycinate – Complements bone structure and muscle health.

Clinical Rationale
Bone health is influenced by multiple nutrients working together — not calcium alone. Modern dietary patterns, reduced sun exposure, aging, and hormonal changes can all impact bone density over time.
Bonoxil is designed with a synergistic nutrient approach, supporting:
Bone mineral density
Structural strength
Calcium metabolism
Musculoskeletal function
Core Advantages
✅ Superior Calcium Absorption
Uses calcium citrate, a well-tolerated form known for better absorption compared to commonly used calcium salts and suitable even for individuals with lower gastric acidity.
✅ Directs Calcium to Bones — Not Soft Tissues
Vitamin K2-7 plays an important role in activating proteins that help guide calcium into bone matrix while supporting vascular health.
✅ Enhances Calcium Utilization
Vitamin D3 assists in intestinal calcium absorption and contributes to maintaining adequate serum calcium levels.
✅ Supports Muscle Function
Magnesium bisglycinate helps support neuromuscular activity and complements calcium in maintaining normal muscle performance.
✅ Designed for Long-Term Bone Maintenance
Appropriate for preventive nutrition strategies where sustained skeletal support is recommended.
✅ Gentle on the Stomach
Calcium citrate is typically associated with better gastrointestinal tolerance than some traditional calcium formulations.


